Hi John great work as usual, I just wanted to update Ionic Rare Earths, IXRs, Ionic Technologies
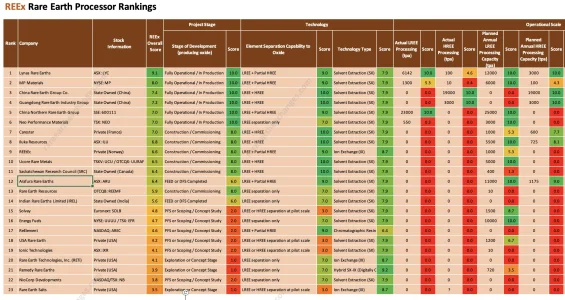
1. The REEx table incorrectly classifies most companies as using
"Solvent Extraction (SX)" technology. Ionic Technologies (ASX: IXR) uses a completely different and innovative technology:
Multifunctional Amide Ionic Liquids (MAIL) Technology
- NOT Solvent Extraction (SX)
- Uses Multifunctional Amide Ionic Liquids for rare earth separation
- Patented ligand engineering technology developed at Queens University Belfast
- Two orders of magnitude higher selectivity than conventional methods.
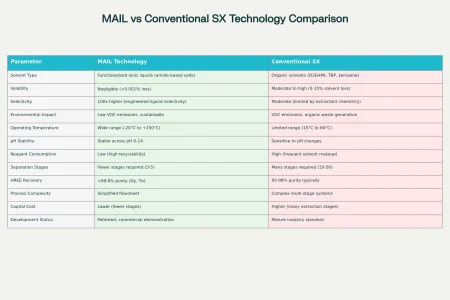
Multifunctional Amide Ionic Liquids (MAIL) Technology Overview:
1.
Ionic Liquids as Solvents: MAIL uses ionic liquids—salts in the liquid state at near ambient temperatures—that serve as non-volatile, highly tunable solvents for rare earth metal separation. Unlike traditional SX solvents, these ionic liquids can be engineered to possess specific chemical functionalities that enhance selectivity and efficiency for rare earth ions.
2.
Amide Functional Groups: The ionic liquids used by Ionic Technologies are functionalized with amide groups, which act as ligands that bind selectively to specific rare earth ions. This selective binding enhances separation efficacy between light rare earth elements (LREE) and heavy rare earth elements (HREE).
3.
Ligand Engineering: Through advanced ligand engineering, the chemical structure of the amide ionic liquids is optimized to improve RE selectivity, stability, and recyclability. This involves designing molecules that target specific rare earth ions such as neodymium, praseodymium (LREE), dysprosium, and terbium (HREE) with high binding strength and selectivity.
4.
Higher Selectivity and Sustainability: MAIL technology achieves separation selectivity up to two orders of magnitude higher than conventional SX processes. This improved selectivity also reduces chemical waste and reagent consumption, making the process more sustainable and environmentally friendly.
5.
Patented and Developed at Queen’s University Belfast: The MAIL technology is patented and was developed with significant scientific input from Queen’s University Belfast. The company has commercialized this technology for magnet rare earth recycling and separation.
 First-of-its-kind
First-of-its-kind technology for individual magnet rare earth recycling.
Operational Status: FULLY OPERATIONAL Since January 2024
Current Production Capacity,
- Demonstration Plant: 10 tonnes per annum (tpa) capacity - OPERATIONAL since January 2024
- 24/7 continuous operation since January 1, 2024
Currently producing high-purity separated REOs:
- LREE: NdPr oxide (Didymium) at >99.8% purity
- HREE: Dy₂O₃ (Dysprosium oxide) at >99.8% purity
- HREE: Tb₄O₇ (Terbium oxide) at >99.5% purity
Scaling to Commercial Production
- Commercial plant capacity: 400tpa (40-fold increase from demo plant)
Planned production breakdown:
- 350 tpa LREE (NdPr oxide)
- 37 tpa Dysprosium oxide
- 13 tpa Terbium oxide
- Construction timeline: Completion by late 2026
- First production: Early 2027
Ionic Technologies represents a
paradigm shift in rare earth processing technology and should be prominently featured in any comprehensive ranking of global rare earth processors. The company's
operational demonstration plant,
innovative MAIL technology,
strong government backing, and
clear path to commercial scale make it a critical player that the REEx table has completely overlooked.
This omission significantly undermines the credibility of the REEx rankings, particularly given Ionic Technologies'
unique position as the
only Western facility currently producing separated magnet rare earth oxides at commercial purity levels.
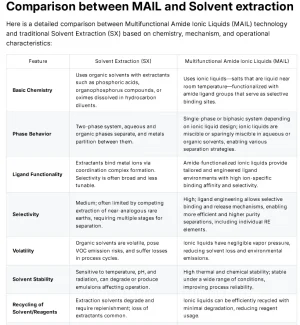
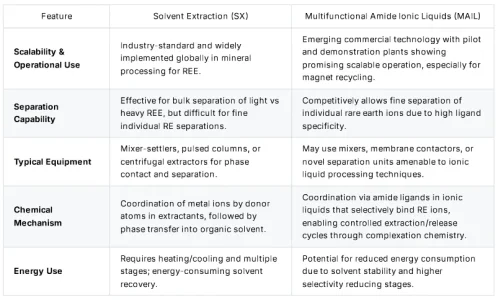
This comprehensive comparison demonstrates that
MAIL technology represents a fundamental advancement beyond conventional solvent extraction, offering superior selectivity, sustainability, and economic benefits for rare earth processing, Also can used on
MIXED RARE EARTH CARBONATES and other RARE EARTH MINING CONCENTRATES.